Oxygen therapy devices
Introduction
There are different mechanisms to supply O2, each of them with precise indications and its own advantages and disadvantages.
Oxygen therapy devices are understood as the interfaces that will carry oxygen from the source to the patient’s airway.
The device to be selected will depend on the characteristics and needs of the patient. It must be selected properly since the effectiveness of the therapy is determined based on it.
Among the aspects to be evaluated are the required flow (8) or O2 concentration, degree of compliance, activity and individual characteristics.
The most used criterion to classify oxygen therapy systems is the flow rate of the gas mixture that reaches the individual: low and high flow.
Oxygen therapy systems
Low flow
These systems are characterized in that the patient inhales O2-enriched air at the same time as ambient air. Because they deliver pure O2 at a flow less than the patient’s inspiratory flow.
It is indicated in users with respiratory capacity with a stable pattern, respiratory rate and tidal volume within normal ranges. The resulting FiO2 (7) is variable, both high and low, and depends on the flow of oxygen and the ventilatory pattern.
Therefore, the criterion for the use of low-flow therapy is primarily that the user is aware and cooperative.
Most used low flow systems
- Nasal cannulas or goggles.
- Simple mask.

Nasal cannulas
Indications
- Patients with oxygen needs at low concentrations.
- Acute or chronic disease with hypoxemia (11) and mild respiratory distress.
- Long-term oxygen therapy (home oxygen therapy).
- Post anesthesia recovery.
Characteristic
- It is the simplest, most widely used and best accepted oxygen administration interface for the patient.
- Made of light and flexible plastic tubes, it consists of an extension of two tips of between 0.5-1 cm that adapt to the nostrils and stay in the ears.
- It allows talking, eating, sleeping and expectorating without interrupting the oxygen supply.
- They have a low economic cost.
- Does not contain latex.
Flow and FiO2
- This device increases the inspired O2 concentration by 3-4% for every liter/min of oxygen delivered.
- It should be supplied between 1-4 litres/min. Reaching FiO2 levels of 24-36% of 02, in adults.
- An approximate formula for calculating FiO2 has been determined:
FiO2= 20 + [4 * Flow rate (litres/min)].
Drawbacks
- It is not possible to determine the exact FiO2 delivered.
- Its effectiveness decreases during mouth breaths or during sleep.
- Its use is not recommended at flows greater than 4 l/min because the rapid flow of oxygen causes dryness, epistaxis and irritation of the nasal passages and does not increase the concentration of inspired O2.
Nursing care
- Periodically check the position and fit of the nasal cannula.
- Check that the user’s nostrils are patent, free of secretions.
- Monitor the support points of the cannula, especially in the ears and nasal mucosa.
- Regularly check the agreement between the prescribed flow and the O2 supply.
- Keep the device clean and throw it away if it gets dirty or damaged.
- Check that the connections, especially in the case of using extension cords, are working properly and that the cords are not pinched by wheels, chairs, or other materials in the room.
- Promote oral and nasal hygiene.
- Facilitate oral hydration.
- Lubricate the nasal mucous membranes with aqueous solutions, not with oil or Vaseline.
- Perform periodic check through pulse oximeter and record.
Simple mask
Indication
- Patients with acute or chronic lung disease with hypoxemia or mild to moderate respiratory distress.
- During minor emergency transportation.
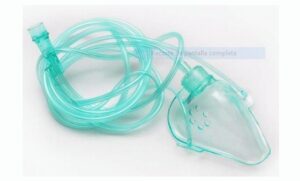
Characteristic
- It has lateral holes that allow the exhaled volume of air to exit through one-way valves that make it difficult for ambient air to enter during inspiration.
- It covers the patient’s nose, mouth and chin. It adjusts through the back strap and front metal pin.
- Simple and light.
- Does not contain latex.
Flow and FiO2
- This device allows reaching an approximate FiO2 between 40-60%, at a flow rate of 5-8 litres/min.
- A minimum flow rate of 5 litres/min must be maintained to avoid re-inhalation of CO2.
- Its use is not recommended for flows greater than 8 L/min because it does not increase the administered FiO2.
Drawbacks
- Little comfortable and generally poorly tolerated.
- During feeding periods it should be replaced by nasal cannulae.
- Difficult oral communication.
- It is not possible to determine the exact FiO2 delivered.
- Difficulty expectorating.
- Uncomfortable in trauma or facial burns.
Nursing care
- Watch for possible air leaks, mainly towards the user’s eyes.
- Prevent skin irritation and pressure ulcers.
- Assess the nasal and oral mucosa and moisturize if necessary.
- Regularly check that the mask is in the correct position.
- Evaluate the support points of the mask and accessories, in order to prevent injuries and pressure ulcers.
- Protect if necessary.
- Regularly check the agreement between the prescribed flow and the O2 supply.
- Check that the connections, especially in the case of using extension cords, are working properly and that the cords are not pinched by wheels, chairs, or other materials in the room.
- Keep the device clean and throw it away if it gets dirty or damaged.
- Promote oral and nasal hygiene.
- Facilitate oral hydration.
- Lubricate the nasal mucous membranes with aqueous solutions, not with oil or Vaseline.
- Perform periodic check through pulse oximeter and record.
See full article: https://enfermeriabuenosaires.com/dispositivos-de-oxigenoterapia/
Oxygen therapy devices
Author information
- Guía rápida y póster de dispositivos de oxigenoterapia para enfermería. Nahia Arraiza Gulina. Director/a: Elena Irigaray Oses. Asesora: Sandra Burguete Gallo. Universidad Pública de Navarra. Curso 2014-2015
- Lorena Plazas. Lic. en enfermería. Trabajo propio.
- https://stening.com.ar
- https://www.medicalexpo.es/prod/nice-neotech-medical-systems/product-98341-675466.html. Imágenes
- https://web.archive.org/web/20181202142038/https://www.medicalcenter.com.mx/ reservorio-para-adulto. Imagen
- https://www.iberomed.es/blog/2018/02/28/que-son-y-para-que-sirven-los-resucitadores manuales/Imagen
- https://www.rd.com
- https://breathefreely.com
Last update: [ 09/20/2022 ]